 Dilantin (Phenytoin) is one of the oldest antiepileptic drugs available in the United States. It was developed over one hundred years ago to treat victims of electroshock therapy.
Dilantin (Phenytoin) is one of the oldest antiepileptic drugs available in the United States. It was developed over one hundred years ago to treat victims of electroshock therapy.
The drug works by decreasing the speed of the electrical signals between the body and brain, ultimately helping to control seizures.
By 1940 doctors discovered that the drug was an effective treatment against various forms of epilepsy, cementing its place in the medical community.
However, Dilantin has been associated with several severe long term side effects, including severe allergic reactions and several forms of brain atrophy.
Specific side effects associated with Dilantin include diplopia, dysarthria, lack of coordination, drowsiness, and focal cerebral atrophy, or cerebellar atrophy.
The brain atrophy conditions are linked to cerebral degeneration, which can affect the patient’s movement, coordination, and speech.
Overview of Dilantin Focal Cerebral Atrophy and Cerebellar Atrophy
Cerebral atrophy occurs when the brain’s tissue starts to deteriorate, and loses neurons and the ability to connect them. This condition can be generalized, affecting the entire organ, or it can be focal, affecting only a certain area of the brain.
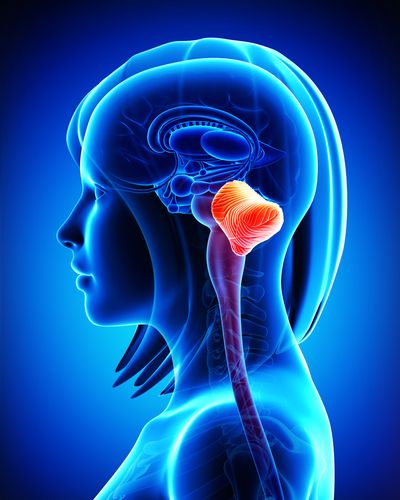
Cerebellar atrophy specifically describes the deterioration of the cerebellum, a portion of the brain that sits under the cerebrum behind the brain stem, controlling muscle coordination. Cerebellar atrophy affects the patient’s posture, coordination, and speech.
Multiple studies have linked long term Dilantin use to brain atrophy. At this point in time, experts are unsure why Dilantin may be inducing these reactions, but suspect it is linked to drug toxicity of the brain.
A study published in 2003 found that moderate to severe atrophy was linked to long term use of Dilantin. A 2007 study utilizing MRI diagnostic images also showed that Dilantin may cause cerebral atrophy.
Research shows that these conditions generally appear in patients with higher amounts of phenytoin, Dilantin’s main ingredient, in their systems. Some cases of brain atrophy have also been observed in patients within normal therapeutic ranges though.
Dilantin patients who have suffered from cerebral atrophy or cerebellar atrophy may be eligible to take legal action against the drug’s manufacturer. Potential claimants should contact a specialized lawyer to determine if they are eligible to file lawsuit.
In general, phenytoin lawsuits are filed individually by each plaintiff and are not class actions.
Do YOU have a legal claim? Fill out the form on this page now for a free, immediate, and confidential case evaluation. The attorneys who work with Top Class Actions will contact you if you qualify to let you know if an individual Dilantin lawsuit or Dilantin class action lawsuit is best for you. Hurry — statutes of limitations may apply.
ATTORNEY ADVERTISING
Top Class Actions is a Proud Member of the American Bar Association
LEGAL INFORMATION IS NOT LEGAL ADVICE
Top Class Actions Legal Statement
©2008 – 2025 Top Class Actions® LLC
Various Trademarks held by their respective owners
This website is not intended for viewing or usage by European Union citizens.
Get Help – It’s Free
Join a Free Dilantin, Phenytoin Cerebral Atrophy Class Action Lawsuit Investigation
If you or a loved one were injured by Dilantin/phenytoin side effects, you may have a legal claim. Fill out the form for a free case evaluation.
An attorney will contact you if you qualify to discuss the details of your potential case.
Oops! We could not locate your form.












